PANCHAKARMA
What is Panchakarma?
Panchakarma is a key detoxification and rejuvenation therapy in Ayurveda. The term “Panchakarma” comes from Sanskrit, where “Pancha” means five, and “Karma” means actions or procedures. Thus, Panchakarma refers to the five therapeutic actions designed to cleanse the body of toxins, balance the doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha), and promote overall health and well-being.
The Five Procedures of Panchakarma
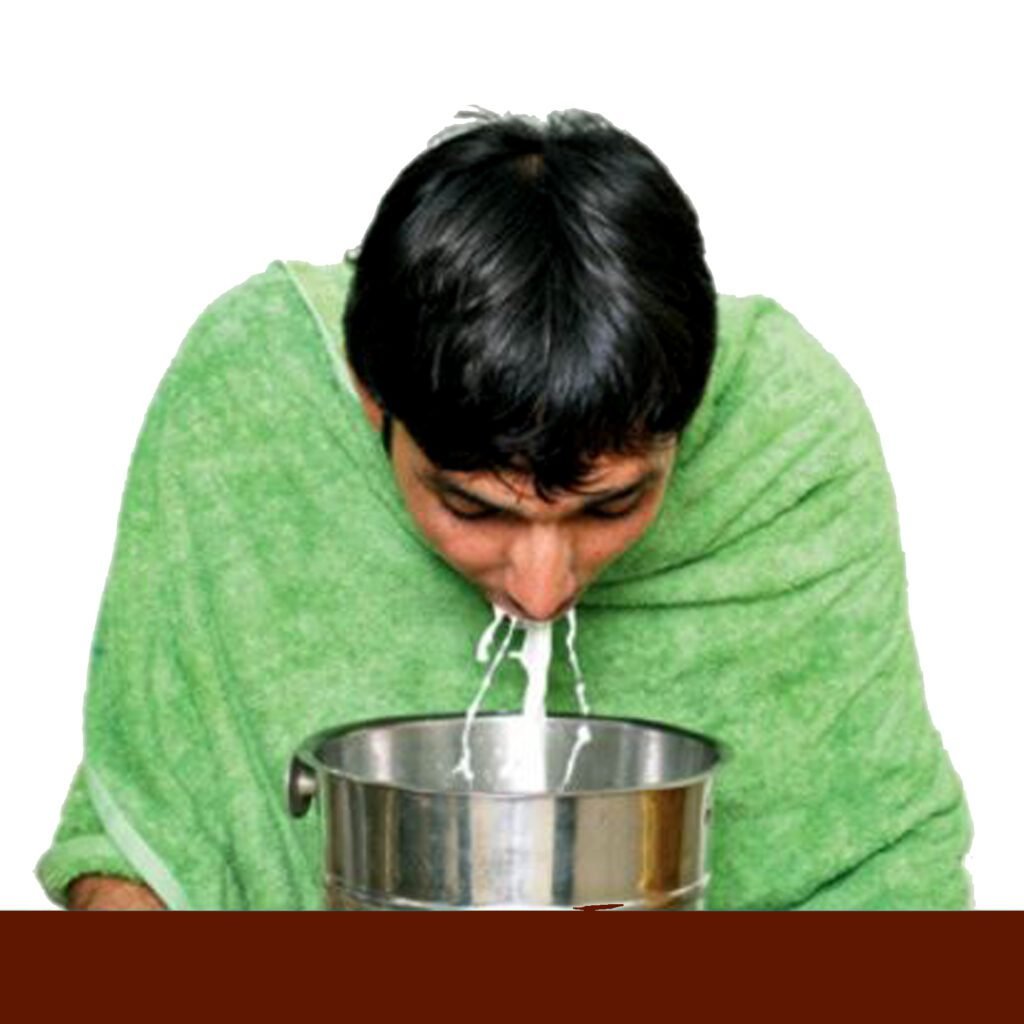

1. Vamana (Therapeutic Emesis):
This is a controlled vomiting process that helps eliminate excess Kapha dosha from the body. It is typically recommended for conditions like asthma, chronic sinusitis, and certain skin disorders. Vamana aims to clear the upper digestive tract and respiratory system of toxins and mucus.

2. Virechana (Purgation Therapy):
Virechana involves the use of herbal laxatives to cleanse the intestines and expel excess Pitta dosha from the body. It is often used to treat digestive issues, skin diseases, and liver disorders. The goal is to detoxify the liver, gallbladder, and small intestine.
3. Basti (Enema Therapy):
Basti is a therapeutic enema that involves administering herbal oils or decoctions into the rectum. This treatment is particularly effective in balancing Vata dosha and is used to treat various conditions, such as arthritis, constipation, and neurological disorders. Basti is considered one of the most important Panchakarma therapies due to its ability to remove deep-seated toxins and nourish the body.

4. Nasya (Nasal Administration):
Nasya involves the administration of medicated oils or powders through the nasal passages. This therapy is used to cleanse the head and sinuses, effectively balancing Kapha and Vata doshas. Nasya is often recommended for headaches, sinusitis, allergies, and respiratory problems.
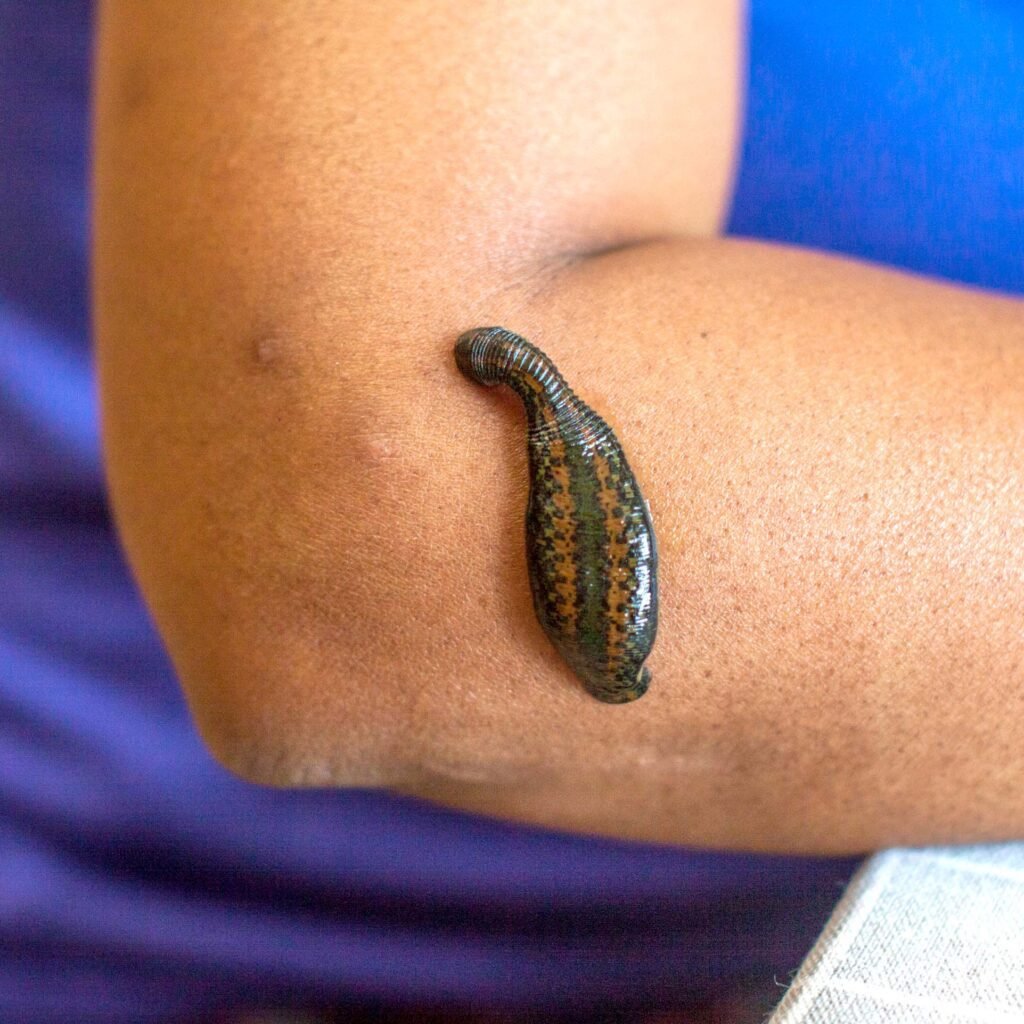

5. Raktamokshana (Bloodletting):
Raktamokshana is a procedure used to cleanse the blood of toxins and is considered a specific treatment for certain blood-related disorders. This therapy can be done using methods like leech therapy or venesection (removal of a small quantity of blood). It is typically used to treat conditions involving blood impurities, such as skin diseases, gout, and certain chronic conditions.
Benefits of Panchakarma
- Restoring Balance: It balances the doshas, enhancing physical and mental well-being.
- Rejuvenation: The therapies help rejuvenate the body’s tissues (Dhatus), enhancing vitality and strength.
- Disease Prevention and Cure: Panchakarma is used both as a preventive measure and a treatment for various chronic and acute conditions.
- Mental Clarity and Relaxation: The process supports mental clarity, relaxation, and stress relief.
Procedure of Panchakarma
The Panchakarma treatment typically involves three stages:
- Purvakarma (Preparatory Phase): This phase includes Snehana (internal and external oleation or oil application) and Swedana (sudation or sweating) to prepare the body for the main detoxification process. These procedures help loosen toxins and facilitate their removal from the tissues.
- Pradhanakarma (Main Phase): This is the phase where the actual Panchakarma therapies (Vamana, Virechana, Basti, Nasya, Raktamokshana) are performed according to the individual’s needs and dosha imbalances.
- Paschatkarma (Post-Procedure Phase): After the main detoxification process, this phase involves dietary and lifestyle modifications to help the body recover, rejuvenate, and maintain the benefits of Panchakarma. It includes a gradual reintroduction of regular foods and activities, along with specific guidelines to prevent the recurrence of toxins and imbalances.
Panchakarma should always be performed under the guidance of a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner, as the procedures need to be carefully customized to each individual’s constitution and health condition.